DAHUA UTP CAT6 NETWORK CABLE (DH-PFM920-6UN)
₱7,350.00
· 305 m (1000 ft)/carton UTP CAT6, power over Ethernet, compatible
with one cable
· High-purity oxygen-free copper conductor
· Customized flame retardant PVC outer sheath
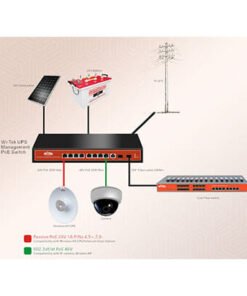
System Overview
Network cables are the most commonly used transmission mediums in
generic cabling system. It is usually composed of 4 pairs of twisted wires,
and is generally applied in system cabling within 100 meters.
Technical Specification
Conductor
Material Oxygen free copper (99.97% purity)
Diameter 0.52 mm ± 0.02 mm
American Wire Gauge 24 AWG
Insulation
Material HDPE
Diameter 0.92 mm ± 0.02 mm
Color (4 Pairs) Blue, white/blue; orange, white/orange; green,
white/green; brown, white/brown
Separator
Material PE
Specification Translucent 4.3 × 0.35 mm
Rip Cord
Material Nylon
Specification 450D
Sheath
Material FR-PVC
Min. Average Thickness 0.5 mm
Diameter 5.8 mm ± 0.2 mm
Color Blue
Electrical
Max. DC Resistance of a Single
Conductor(+20℃) 9Ω/100 m
Min. Insulation Resistance 5000MΩ·km
Max. DC Resistance Unbalance 2% (pair intra), 4% (pairs inter)
Dielectric Strength No breakdown with 1KV DC for 1 min
Transmission
Characteristic Impedance 100 ± 15Ω
Near End Cross Talk ≥39.30 dB/100 m@250 MHz
Max. Attenuation 34.8 dB/100 m@250 MHz
Return Loss ≥17.3 dB/100 m@250 MHz
Mechanical
Tensile Strength Sheath≥13.5 MPa, insulation≥16 MPa
Elongation at Break Sheath≥150%, insulation≥300%
Installation Bending Radius >8 times of outer cable diameter
Conductor Elongation at Break ≥10%
Environmental
Shrinkage of Insulation ≤5%
Color Migration Resistance of
Insulation No migration
Sheath Tensile Strength and
Elongation at Break after
Aging
≥12.5 MPa, ≥100%
Related products
Accessories
24 Port and Up